Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell said Thursday he will not resign if President-elect Donald Trump asks him to, saying the president does not have the legal authority to fire a central bank chief.
However, Chairman Powell’s term expires in May 2026, at which point President Trump will have the opportunity to appoint a new Fed chief. He will also have the opportunity to replace at least one other Fed director during his term.
Let’s take a look at how the structure of the Fed system and the selection of policy makers works.
-
Also read: Fed cuts interest rates as Powell vows not to resign if Trump asks
FRB system
Established by Congress in 1913, the Federal Reserve System consists of the Federal Reserve Board, headquartered in Washington. 12 local federal banks scattered throughout the country. the Federal Open Market Committee, which includes both Federal Reserve Board members and local bank presidents;
The Federal Reserve Board has seven members, including one overall chairman, two vice chairs (one in charge of monetary policy and one in charge of banking supervision), and four other governors. All members are appointed by the president after confirmation by the Senate.
Trump succeeded in appointing four board members during his term, and elevated Powell, who was already the Fed’s governor after being appointed by Trump’s predecessor, Democrat Barack Obama, to chair the Fed.
All of his successful appointments, including Mr. Powell and current governors Michelle Bowman and Christopher Waller, have held true to the Fed’s tradition of independence. Three others who many saw as pushing the envelope, Stephen Moore, Judith Shelton and Herman Cain, either withdrew or failed to gain full Senate confirmation. .
Each regional Fed bank is run by a president appointed by a subcommittee of each bank’s board of directors.
The FOMC, which plays a vital role in determining interest rate policy, is made up of a rotating body of seven directors, the president of the New York Fed, and four other regional bank presidents.
current board
Federal Reserve Board members are appointed by the President for a 14-year term, or for the remainder of a 14-year term in the case of a former incumbent, and are confirmed by the Senate. Term expirations will be phased in every two years, with the next term expiration scheduled for 2026.
The Fed chair and vice chair are appointed for four-year terms concurrently with the Fed’s leadership role and generally do not remain in the role unless reappointed to a leadership role. Powell’s chairmanship will expire in May 2026, and the positions of both vice chairs will expire during the term of the next U.S. president.
Below is a list of current governors, ordered by those closest to the end of their terms.
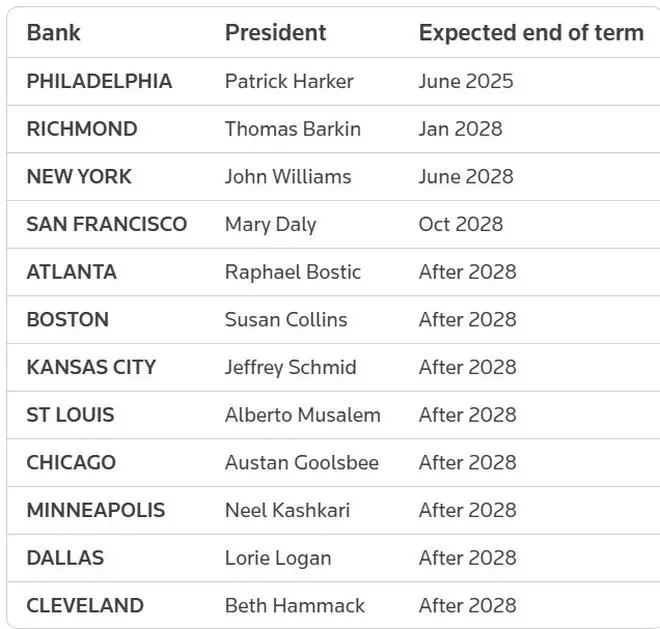
Current status of bank president
The Fed president is elected by six non-banker members of the board of directors and must be approved by the Fed’s board of directors. They can serve until the retirement age of 65 years, or for 10 years if appointed after the age of 55, or until they reach the age of 75.
The terms of all current bank presidents will end in February 2026, and new five-year appointments will be considered by the board. Although this reappointment process has not historically resulted in a change of leadership, it is customary and not law.
Below is a list of the term limit dates for four local bank presidents whose terms expire during President Trump’s next term.